一、酒驾风险行为分析预测
1.背景描述
本数据集来自2007年青少年风险行为监测系统(YRBSS),该系统是由美国疾病控制和预防中心(CDC)进行的年度调查,旨在监测有健康风险的青少年行为的流行情况。
本数据集的重点是青少年最近(在过去30天内)是否乘坐过醉酒司机的车。

2.数据说明
本数据集包含13387条记录,涉及以下6个变量:
- 是否在过去30天内与饮酒驾驶者一起乘车:1=有;0=没有
- 是否是女性:1=女性;0=男性
- 就读年级:9,10,11,12
- 年龄
- 是否吸烟:1=是;0=否
- 是否拥有驾照:1=有;0=没有
3.数据来源
二、数据分析
1.数据读取
import pandas as pd
df=pd.read_csv('data/data225503/Risky_behavior_in_youths.csv',encoding='gbk')
df.head()
.dataframe tbody tr th:only-of-type {
vertical-align: middle;
}
.dataframe tbody tr th {
vertical-align: top;
}
.dataframe thead th {
text-align: right;
}
| 序号 | 是否在过去30天内与饮酒驾驶者一起乘车 | 是否是女性 | 就读年级 | 年龄 | 是否吸烟 | 是否拥有驾照 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1.0 | 10.0 | 15.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 |
| 1 | 2 | 1 | 1.0 | 10.0 | 18.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| 2 | 3 | 1 | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 3 | 4 | 0 | 0.0 | 11.0 | 17.0 | 0.0 | 1.0 |
| 4 | 5 | 0 | 0.0 | 11.0 | 17.0 | 0.0 | 1.0 |
2.空值处理
df.isnull().sum()
序号 0
是否在过去30天内与饮酒驾驶者一起乘车 0
是否是女性 755
就读年级 67
年龄 54
是否吸烟 388
是否拥有驾照 54
dtype: int64
df.shape
(13387, 7)
df.isnull().sum()/df.shape[0]
序号 0.000000
是否在过去30天内与饮酒驾驶者一起乘车 0.000000
是否是女性 0.056398
就读年级 0.005005
年龄 0.004034
是否吸烟 0.028983
是否拥有驾照 0.004034
dtype: float64
df.dropna(inplace=True)
df.drop(['序号'], inplace=True, axis=1)
df.shape
(12282, 6)
df.describe()
.dataframe tbody tr th:only-of-type {
vertical-align: middle;
}
.dataframe tbody tr th {
vertical-align: top;
}
.dataframe thead th {
text-align: right;
}
| 是否在过去30天内与饮酒驾驶者一起乘车 | 是否是女性 | 就读年级 | 年龄 | 是否吸烟 | 是否拥有驾照 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| count | 12282.000000 | 12282.000000 | 12282.000000 | 12282.000000 | 12282.000000 | 12282.000000 |
| mean | 0.313385 | 0.525973 | 10.523449 | 16.152337 | 0.535581 | 0.676193 |
| std | 0.463888 | 0.499345 | 1.114185 | 1.209777 | 0.498753 | 0.467946 |
| min | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 9.000000 | 14.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| 25% | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 10.000000 | 15.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| 50% | 0.000000 | 1.000000 | 11.000000 | 16.000000 | 1.000000 | 1.000000 |
| 75% | 1.000000 | 1.000000 | 12.000000 | 17.000000 | 1.000000 | 1.000000 |
| max | 1.000000 | 1.000000 | 12.000000 | 18.000000 | 1.000000 | 1.000000 |
从上表可以看出,
- 经过清洗后,共有12282条数据;
- 在过去30天内与饮酒驾驶者一起乘车占比31.34%;
- 数据中女生人数多于男生,女生人数占比52%;
- 数据中大部分的年级为10、11;
- 年龄均值为16岁;
- 数据中吸烟和有驾照的人为多数,占比分别为53%和67%。
三、数据预处理
1.数据归一化
columns = df.columns
print(columns)
Index(['是否在过去30天内与饮酒驾驶者一起乘车', '是否是女性', '就读年级', '年龄', '是否吸烟', '是否拥有驾照'], dtype='object')
for column in columns[1:]:
col = df[column]
col_min = col.min()
col_max = col.max()
normalized = (col - col_min) / (col_max - col_min)
df[column] = normalized
df.head()
.dataframe tbody tr th:only-of-type {
vertical-align: middle;
}
.dataframe tbody tr th {
vertical-align: top;
}
.dataframe thead th {
text-align: right;
}
| 是否在过去30天内与饮酒驾驶者一起乘车 | 是否是女性 | 就读年级 | 年龄 | 是否吸烟 | 是否拥有驾照 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 1.0 | 0.333333 | 0.25 | 1.0 | 0.0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1.0 | 0.333333 | 1.00 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| 3 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.666667 | 0.75 | 0.0 | 1.0 |
| 4 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.666667 | 0.75 | 0.0 | 1.0 |
| 5 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.666667 | 0.75 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
2.数据集切分
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# 切分数据集为 训练集 、 测试集
train, test = train_test_split(df, test_size=0.2, random_state=2023)
3.协相关
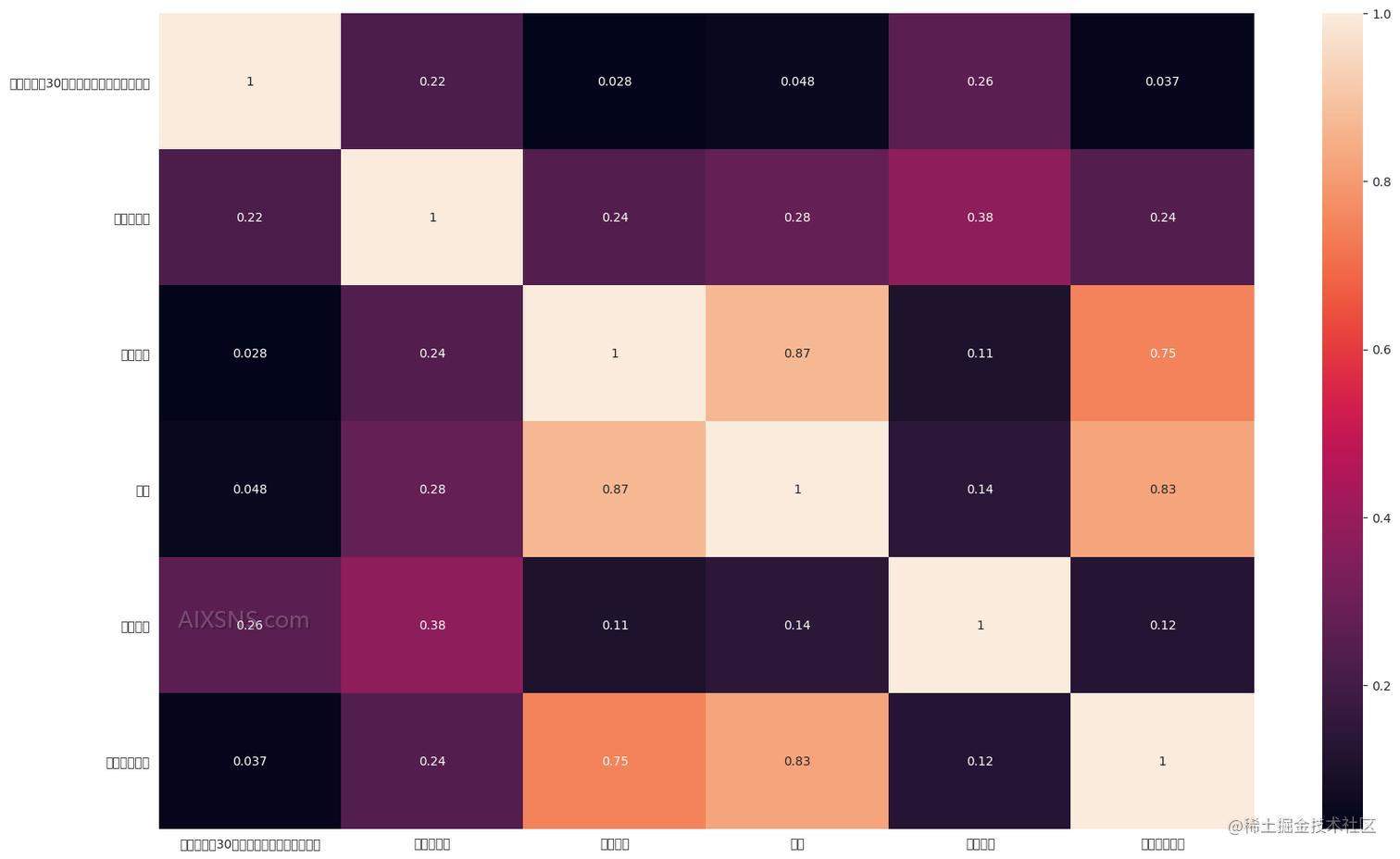
df.corr()
.dataframe tbody tr th:only-of-type {
vertical-align: middle;
}
.dataframe tbody tr th {
vertical-align: top;
}
.dataframe thead th {
text-align: right;
}
| 是否在过去30天内与饮酒驾驶者一起乘车 | 是否是女性 | 就读年级 | 年龄 | 是否吸烟 | 是否拥有驾照 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 是否在过去30天内与饮酒驾驶者一起乘车 | 1.000000 | 0.220942 | 0.028239 | 0.048411 | 0.258869 | 0.037261 |
| 是否是女性 | 0.220942 | 1.000000 | 0.240245 | 0.282104 | 0.377348 | 0.238284 |
| 就读年级 | 0.028239 | 0.240245 | 1.000000 | 0.870475 | 0.107223 | 0.748354 |
| 年龄 | 0.048411 | 0.282104 | 0.870475 | 1.000000 | 0.142229 | 0.825015 |
| 是否吸烟 | 0.258869 | 0.377348 | 0.107223 | 0.142229 | 1.000000 | 0.123856 |
| 是否拥有驾照 | 0.037261 | 0.238284 | 0.748354 | 0.825015 | 0.123856 | 1.000000 |
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
import seaborn as sns
sns.set_style('whitegrid')
# 热力图
plt.figure(figsize=(20,12))
sns.heatmap(df.corr(), annot=True)
四、模型训练
1.网络定义
import paddle
import paddle.nn.functional as F
# 定义动态图
class Net(paddle.nn.Layer):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
# 定义一层全连接层,输出维度是1,激活函数为None,即不使用激活函数
self.fc = paddle.nn.Linear(in_features=5,out_features=2)
# 网络的前向计算函数
def forward(self, inputs):
pred = self.fc(inputs)
return pred
2.超参设置
net=Net()
# 设置迭代次数
epochs = 6
# paddle.nn.loss.CrossEntropyLoss正常
# paddle.nn.CrossEntropyLoss不正常
loss_func = paddle.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
#优化器
opt = paddle.optimizer.Adam(learning_rate=0.1,parameters=net.parameters())
3.模型训练
#训练程序
for epoch in range(epochs):
all_acc = 0
for i in range(train.shape[0]):
x = paddle.to_tensor([train.iloc[i,1:]])
y = paddle.to_tensor([train.iloc[i,0]])
infer_y = net(x)
loss = loss_func(infer_y,y)
loss.backward()
y=label = paddle.to_tensor([y], dtype="int64")
acc= paddle.metric.accuracy(infer_y, y)
all_acc=all_acc+acc.numpy()
opt.step()
opt.clear_gradients#清除梯度
# print("epoch: {}, loss is: {},acc is:{}".format(epoch, loss.numpy(),acc.numpy())) #由于输出过长,这里注释掉了
print("第{}次正确率为:{}".format(epoch+1,all_acc/i))
第1次正确率为:[0.6094259]
第2次正确率为:[0.6070847]
第3次正确率为:[0.5988396]
第4次正确率为:[0.61268324]
第5次正确率为:[0.61115634]
第6次正确率为:[0.5905945]
五、模型评估
1.模型训练
#测试集数据运行
net.eval()#模型转换为测试模式
all_acc = 0
for i in range(test.shape[0]):
x = paddle.to_tensor([test.iloc[i,:-1]])
y = paddle.to_tensor([test.iloc[i,-1]])
infer_y = net(x)
y=label = paddle.to_tensor([y], dtype="int64")
# 计算损失与精度
loss = loss_func(infer_y, y)
acc = paddle.metric.accuracy(infer_y, y)
all_acc = all_acc+acc.numpy()
# 打印信息
#print("loss is: {}, acc is: {}".format(loss.numpy(), acc.numpy()))
print("测试集正确率:{}".format(all_acc/i))
测试集正确率:[0.44177523]
2.预测
import numpy as np
#预测结果展示
net.eval()
x = paddle.to_tensor([test.iloc[0,1:]])
y = paddle.to_tensor([test.iloc[0,0]])
infer_y = net(x)
y=label = paddle.to_tensor([y], dtype="int64")
# 计算损失与精度
loss = loss_func(infer_y, y)
# 打印信息
print("test[0] is :n{}n y_test[0] is :{}n predict is {}".format(test.iloc[0,1:] ,test.iloc[0,0], np.argmax(infer_y.numpy()[0])))
test[0] is :
是否是女性 0.00
就读年级 1.00
年龄 0.75
是否吸烟 1.00
是否拥有驾照 1.00
Name: 481, dtype: float64
y_test[0] is :0
predict is 0

